Cloud Storage Pricing Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide
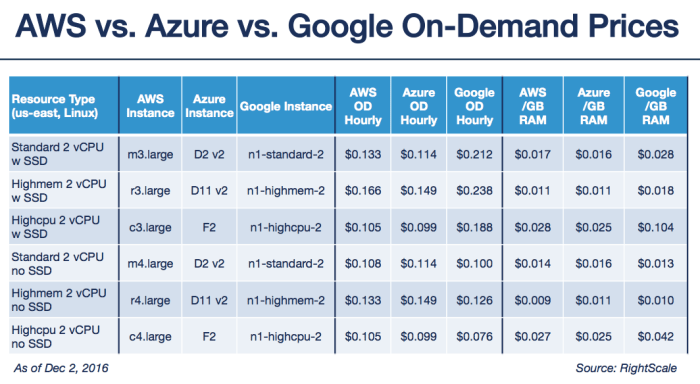
In today’s data-driven world, cloud storage has become indispensable for businesses and individuals alike. With its scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, cloud storage offers a compelling solution for data management and backup. However, navigating the various pricing models and providers can be a daunting task.
This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth analysis of cloud storage pricing, empowering you to make informed decisions and optimize your storage costs.
We will delve into the different pricing structures, key factors to consider, and top providers in the market. Additionally, we will explore cost optimization strategies, security considerations, and best practices to help you maximize the value of your cloud storage investment.
Introduction
Cloud storage is a service model in which data is stored in remote servers accessed over the internet. It offers numerous benefits, including:
- Scalability: Cloud storage can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing storage needs.
- Reliability: Cloud storage providers maintain redundant copies of data to ensure high availability and durability.
- Security: Cloud storage services implement robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud storage eliminates the need for physical storage infrastructure, reducing capital and operational expenses.
This article compares the pricing of different cloud storage providers to help you make an informed decision about which service is right for you.
Pricing Structures
Cloud storage providers offer a variety of pricing structures to meet the diverse needs of their customers. The most common pricing models are per-gigabyte (GB) pricing, per-month pricing, and hybrid pricing.
The choice of pricing structure depends on several factors, including the amount of data to be stored, the frequency of data access, and the budget constraints of the customer.
Per-gigabyte (GB) Pricing
Per-gigabyte pricing is a simple and straightforward pricing model. Customers are charged a fixed amount for each gigabyte of data stored in the cloud.
This pricing model is well-suited for customers who store large amounts of data that are accessed infrequently.
Per-month Pricing
Per-month pricing is a subscription-based pricing model. Customers pay a fixed monthly fee for a certain amount of storage space.
This pricing model is well-suited for customers who store small to medium amounts of data that are accessed frequently.
Hybrid Pricing
Hybrid pricing is a combination of per-gigabyte pricing and per-month pricing. Customers pay a fixed monthly fee for a certain amount of storage space, and then they are charged an additional fee for any additional data stored beyond the included amount.
This pricing model is well-suited for customers who store large amounts of data and have varying access patterns.
Key Factors to Consider
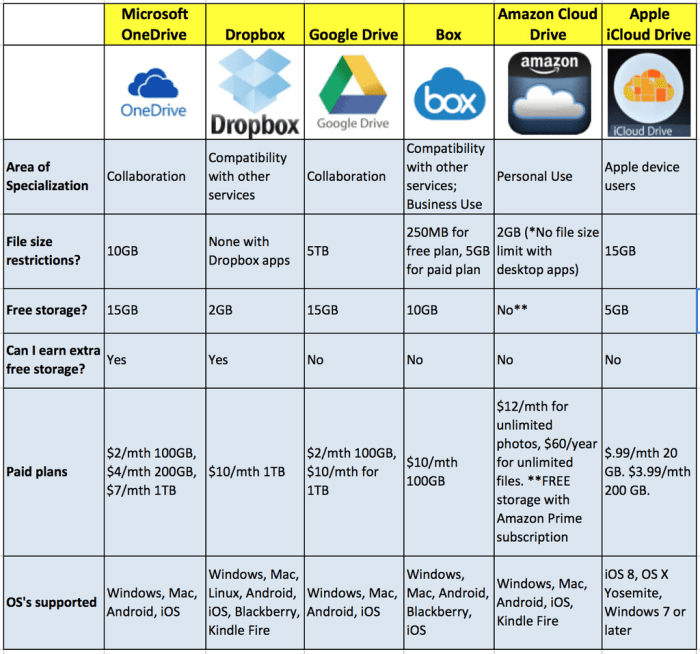
When comparing cloud storage pricing, there are a few key factors to keep in mind:
Monthly vs Annual Commitments
Many cloud storage providers offer discounts for customers who commit to purchasing storage on a monthly or annual basis. These discounts can be significant, so it’s important to factor them into your decision-making process.
Data Ingress/Egress Fees
Some cloud storage providers charge fees for data ingress (moving data into the cloud) and/or data egress (moving data out of the cloud). These fees can add up quickly, so it’s important to be aware of them before you make a decision.
Hidden Fees
It’s important to read the fine print before you commit to any cloud storage provider. Some providers may have hidden fees that can increase your costs down the road.
Security and Reliability Considerations
When choosing a cloud storage provider, it’s crucial to consider the security and reliability measures they offer to protect your data and ensure its availability.
Key factors to evaluate include data encryption, access controls, and data backup and redundancy strategies.
Data Security Features
- Encryption at Rest: Data is encrypted while stored on the provider’s servers, protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Encryption in Transit: Data is encrypted during transfer between devices and the cloud, preventing interception.
- Access Controls: Role-based access control (RBAC) allows you to restrict access to specific users and groups.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Additional security layer that requires multiple forms of authentication to access data.
Uptime Guarantees
Cloud storage providers offer uptime guarantees, ensuring a certain level of service availability. This is critical for businesses that rely on cloud storage for mission-critical applications.
Data Backup and Redundancy
Data backup and redundancy measures ensure that your data is protected in case of hardware failures or disasters.
- Data Replication: Data is stored in multiple geographic locations, providing redundancy and reducing the risk of data loss.
- Snapshots: Point-in-time copies of your data, allowing you to recover data to a specific point in time.
- Versioning: Multiple versions of your files are stored, allowing you to restore previous versions in case of accidental deletions or modifications.
7. Use Cases and Best Practices
Cloud storage solutions offer a wide range of use cases, catering to both business and personal needs. Understanding the specific requirements and adopting best practices for data management can help organizations and individuals maximize the benefits of cloud storage.
Business Use Cases
- Data Backup and Recovery: Cloud storage provides a secure and reliable backup destination for critical business data, ensuring quick and efficient recovery in the event of data loss or system failures.
- Collaboration and File Sharing: Cloud storage platforms facilitate easy collaboration among team members, allowing them to share and access files remotely from any device.
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Cloud storage provides scalable and cost-effective storage for large datasets used in data analytics and machine learning applications.
- Cloud-Native Applications: Cloud storage is an integral component of cloud-native applications, providing seamless integration and scalability.
Personal Use Cases
- Personal Data Backup: Cloud storage offers a convenient way to back up personal data, including photos, videos, and documents, protecting them from device loss or damage.
- File Sharing and Collaboration: Cloud storage platforms allow individuals to easily share files with friends, family, or colleagues, simplifying collaboration and sharing of personal content.
- Media Streaming: Cloud storage can be used to store and stream media content, such as music and videos, providing convenient access to personal entertainment.
Best Practices for Data Management
To ensure optimal performance and security of data stored in the cloud, it is crucial to adopt best practices for data management:
- Data Classification and Organization: Classify data based on its importance, sensitivity, and access requirements to optimize storage and security measures.
- Access Control and Authorization: Implement robust access controls to restrict data access to authorized users and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Establish a data lifecycle management policy to identify and manage data based on its lifecycle stages, ensuring compliance and optimizing storage costs.
- Regular Data Backups: Implement regular data backups to ensure data recovery in the event of accidental deletion or data corruption.
Future Trends

Cloud storage is a rapidly evolving field, and the future holds many exciting possibilities. As data storage technology advances, we can expect to see even more efficient, cost-effective, and secure ways to store our data in the cloud.
One of the most significant trends in cloud storage is the move towards object storage. Object storage is a type of cloud storage that treats data as individual objects, rather than as files or blocks. This makes it easier to manage and access data, and it can also be more cost-effective than traditional file storage.
Pricing Predictions
As the cloud storage market continues to grow, we can expect to see prices continue to fall. This is good news for businesses and consumers alike, as it will make cloud storage more affordable and accessible.
However, it is important to note that not all cloud storage providers are created equal. Some providers may offer lower prices than others, but they may also sacrifice features or security. It is important to do your research and choose a provider that offers the best value for your needs.
Recommendations for Staying Ahead
To stay ahead of the curve in cloud storage, it is important to keep up with the latest trends and technologies. Here are a few recommendations:
- Attend industry events and webinars.
- Read industry blogs and articles.
- Experiment with new cloud storage technologies.
By following these recommendations, you can ensure that you are using the latest and greatest cloud storage technologies to meet your business needs.
Final Summary
Understanding cloud storage pricing is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking to optimize their data management costs. By carefully evaluating the pricing models, considering key factors, and implementing cost-effective strategies, you can make informed decisions that align with your specific needs.
As the cloud storage landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of the latest trends and best practices will ensure that you remain competitive and maximize the potential of this transformative technology.









