Cloud Storage for Medical Records: Revolutionizing Healthcare Data Management

In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, cloud storage has emerged as a transformative force for managing medical records. By leveraging the power of the cloud, healthcare providers can unlock unprecedented benefits, from enhanced accessibility and security to substantial cost savings.
However, the adoption of cloud storage for medical records also presents unique challenges, particularly concerning data privacy and security.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the multifaceted aspects of cloud storage for medical records, exploring its advantages, security considerations, data management strategies, and implementation best practices. We will also examine the future prospects of cloud storage in healthcare and its potential to revolutionize the way medical records are stored, accessed, and shared.
Introduction
Cloud storage has revolutionized the healthcare industry, providing numerous advantages for the storage and management of medical records. By leveraging cloud computing technology, healthcare providers can securely store, access, and share patient data from anywhere with an internet connection.
The benefits of cloud storage for medical records are multifaceted. Improved accessibility allows healthcare professionals to access patient records in real-time, regardless of their location. Enhanced security measures protect sensitive patient data from unauthorized access and data breaches. Cost savings are also realized through reduced hardware and maintenance expenses associated with on-premise storage systems.
Challenges
Despite the advantages, challenges associated with cloud storage for medical records must be acknowledged. Data privacy and security concerns are paramount, as patient information must be protected in accordance with regulatory compliance and ethical guidelines.
Security and Privacy
Ensuring the security and privacy of medical records stored in the cloud is of paramount importance. Failure to do so can result in unauthorized access to sensitive patient information, potentially leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
Additionally, healthcare providers have a legal and ethical obligation to protect patient data.
Security Measures
Various security measures can be implemented to safeguard medical records in the cloud. These include:
- Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit ensures that unauthorized individuals cannot access it, even if they gain access to the cloud storage system.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implementing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, ensures that only authorized individuals can access medical records.
- Access Control: Establishing clear access control policies determines who can access and modify medical records, preventing unauthorized access and misuse.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regular data backups and a robust recovery plan ensure that medical records are not lost in the event of a system failure or data breach.
- Security Monitoring: Continuously monitoring cloud storage systems for suspicious activities and potential security breaches helps detect and respond to threats promptly.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Using cloud storage for medical records raises several legal and ethical considerations, including:
- Compliance with Regulations: Healthcare providers must ensure that their use of cloud storage complies with relevant regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in the European Union.
- Data Ownership and Control: Clarifying who owns and controls the medical records stored in the cloud is crucial to avoid disputes and ensure patient data remains under the control of healthcare providers.
- Patient Consent: Obtaining informed consent from patients before storing their medical records in the cloud is essential to respect their privacy and autonomy.
- Data Breaches: In the event of a data breach, healthcare providers must have a clear plan for notifying affected patients, mitigating the potential consequences, and preventing future breaches.
Data Management
Effective data management is crucial for ensuring the integrity, accessibility, and security of medical records stored in the cloud. It involves organizing, storing, and managing data in a way that allows for efficient retrieval, analysis, and sharing while maintaining data privacy and compliance.
Various data management tools and techniques can be employed in the cloud, including:
- Data lakes: Centralized repositories for storing large volumes of structured and unstructured data, enabling comprehensive analysis and insights.
- Data warehouses: Optimized for structured data, providing fast and efficient querying and reporting capabilities.
- Data governance tools: Establish policies and procedures to ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance.
Challenges of Managing Medical Records in the Cloud
Managing medical records in the cloud presents several challenges:
- Data integration and interoperability: Ensuring seamless data exchange between different systems and applications, despite varying data formats and standards.
- Data security and privacy: Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive medical information from unauthorized access, breaches, and data loss.
- Compliance with regulations: Adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards, such as HIPAA and GDPR, to ensure data protection and patient privacy.
- Data ownership and control: Clearly defining data ownership, access rights, and responsibilities to ensure appropriate stewardship and accountability.
Cloud Storage Options
Medical records can be stored in the cloud in a variety of ways. The most common types of cloud storage options include:
- Public cloud storage: This type of storage is offered by third-party providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Public cloud storage is typically the most cost-effective option, but it may not be as secure as other options.
- Private cloud storage: This type of storage is owned and operated by the organization that uses it. Private cloud storage is more secure than public cloud storage, but it is also more expensive.
- Hybrid cloud storage: This type of storage combines public and private cloud storage. Hybrid cloud storage offers the benefits of both public and private cloud storage, but it can be more complex to manage.
When choosing a cloud storage option for medical records, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Cost: The cost of cloud storage can vary depending on the type of storage, the amount of storage needed, and the provider.
- Security: The security of cloud storage is important for protecting patient data. It is important to choose a provider that has a strong security track record.
- Scalability: The scalability of cloud storage is important for ensuring that the storage can grow as needed. It is important to choose a provider that can offer scalable storage.
Implementation and Adoption
Implementing and adopting cloud storage for medical records involves a series of steps that organizations should follow to ensure a successful transition. These steps typically include:
- Assessment and Planning: Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s current medical record management system, identifying areas for improvement and defining the desired outcomes of cloud storage implementation.
- Vendor Selection: Evaluate and select a cloud storage provider that meets the organization’s specific requirements, considering factors such as security, reliability, scalability, and compliance with industry regulations.
- Data Migration: Develop a comprehensive data migration plan to transfer medical records from the existing system to the cloud storage platform, ensuring data integrity and minimizing disruption to operations.
- System Integration: Integrate the cloud storage platform with the organization’s existing healthcare information systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and practice management systems, to ensure seamless data exchange and access.
- Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training and education to staff on the use and management of the cloud storage system, including data security and privacy protocols.
Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing and adopting cloud storage for medical records can present several challenges, including:
- Security Concerns: Address security concerns related to data privacy, confidentiality, and integrity by implementing robust security measures and adhering to industry best practices.
- Data Interoperability: Ensure data interoperability between the cloud storage platform and other healthcare systems to facilitate seamless data exchange and analysis.
- Cost Management: Optimize cloud storage costs through effective resource allocation, data management strategies, and vendor negotiations.
To overcome these challenges, organizations can adopt the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Security Policies: Develop and implement comprehensive security policies that define data access controls, encryption protocols, and incident response procedures.
- Use Data Encryption: Encrypt medical records at rest and in transit to protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Regularly conduct security audits to identify and address any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the cloud storage system.
- Monitor and Manage Data Access: Implement mechanisms to monitor and manage data access, including role-based permissions and audit trails.
- Collaborate with IT and Security Teams: Foster collaboration between IT and security teams to ensure a comprehensive approach to data protection.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement and adopt cloud storage for medical records, realizing the benefits of improved data management, enhanced security, and increased accessibility while addressing potential challenges and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Future of Cloud Storage for Medical Records
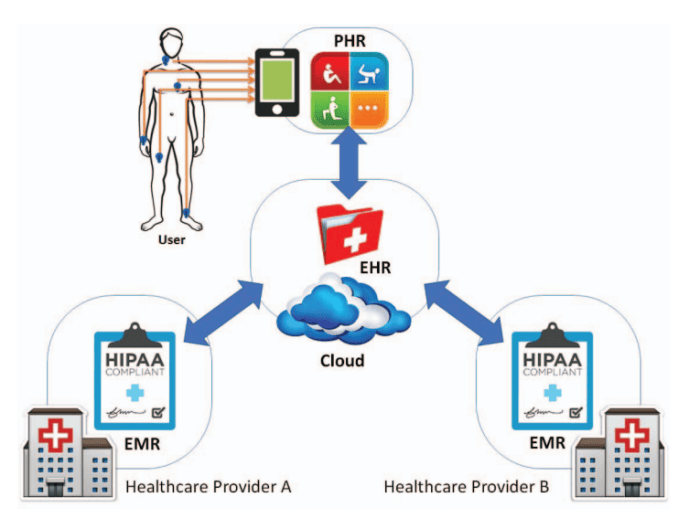
The future of cloud storage for medical records holds immense promise, driven by advancements in technology and the growing adoption of cloud-based solutions in healthcare.Emerging trends and technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain, are poised to revolutionize the way medical records are stored, managed, and utilized.
These technologies offer the potential to enhance data security, improve accessibility, facilitate collaboration, and enable personalized healthcare experiences.
Potential Benefits
*
-*Enhanced data security
Cloud storage providers employ robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect medical records from unauthorized access and data breaches.
-
-*Improved accessibility
Cloud storage allows authorized users to access medical records from anywhere with an internet connection, improving collaboration among healthcare professionals and patient convenience.
-*Increased collaboration
Cloud-based platforms facilitate real-time sharing and collaboration among healthcare providers, enabling seamless communication and coordination of care.
-*Personalized healthcare experiences
AI and ML algorithms can analyze medical records to identify patterns, predict health risks, and tailor treatment plans to individual patients, leading to more personalized and effective healthcare outcomes.
Potential Challenges
*
-*Data privacy concerns
Cloud storage raises concerns about data privacy, as medical records contain sensitive personal information. Addressing these concerns through robust data protection measures and adherence to regulatory compliance is crucial.
-
-*Interoperability challenges
Ensuring interoperability between different cloud storage platforms and legacy systems remains a challenge, hindering seamless data exchange and integration.
-*Cost considerations
Cloud storage services can incur ongoing costs, which healthcare providers need to factor into their budget planning.
-*Regulatory compliance
Cloud storage providers must comply with healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA in the US, to ensure the secure handling and protection of medical records.
Closure

As the healthcare industry continues to embrace digital transformation, cloud storage for medical records will play an increasingly pivotal role. By addressing data security concerns, implementing robust data management strategies, and leveraging the latest technologies, healthcare providers can harness the full potential of cloud storage to enhance patient care, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation in the healthcare sector.









