Discover Papua: The Hidden Gem of Paradise

Introduction to Papua

Papua, also known as Western New Guinea, is the easternmost province of Indonesia, located on the island of New Guinea. The region is known for its rich cultural heritage, diverse wildlife, and breathtaking natural landscapes. Papua is home to over 250 ethnic groups, each with their own unique language, customs, and traditions. The province is also home to some of the most pristine and untouched natural environments in the world, including rainforests, coral reefs, and snow-capped mountains.
Geography and Climate
Papua is situated on the island of New Guinea, which is the second-largest island in the world. The province covers an area of approximately 317,062 square kilometers, making it one of the largest provinces in Indonesia. Papua is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the north, the Arafura Sea to the south, and the Indonesian province of West Papua to the west. The province is characterized by a diverse range of landscapes, including mountains, valleys, and coastal plains. The highest peak in Papua is Puncak Jaya, which is the highest mountain in Indonesia and one of the highest peaks in Southeast Asia.
The climate in Papua is tropical, with high temperatures and high levels of humidity throughout the year. The province experiences a wet season from October to April, and a dry season from May to September. The climate is also influenced by the monsoon winds, which bring heavy rainfall and strong winds to the region during the wet season.
Culture and Traditions
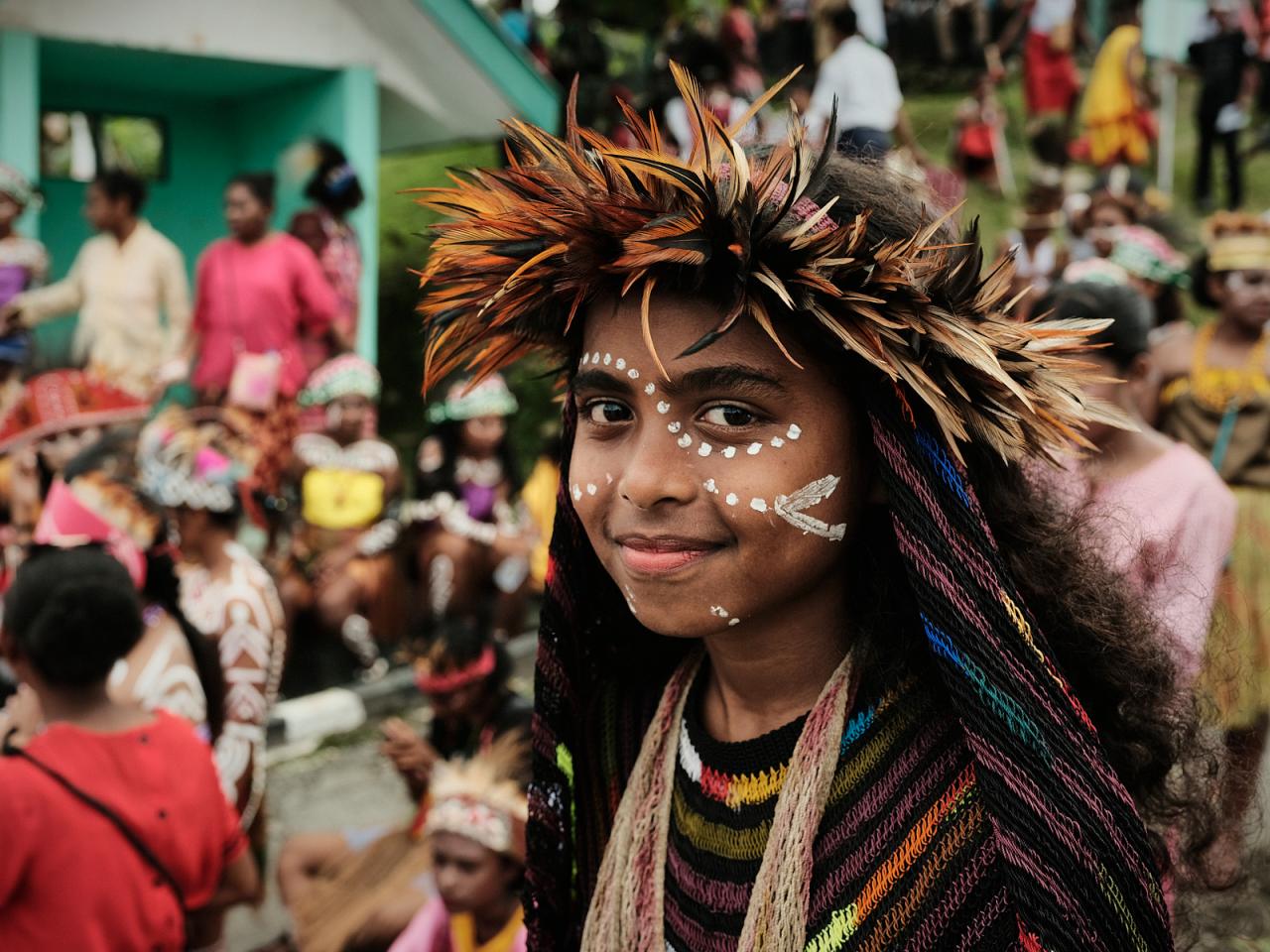
Papua is home to a rich and diverse cultural heritage, with over 250 ethnic groups living in the province. Each ethnic group has its own unique language, customs, and traditions, which are often closely tied to the natural environment. The indigenous people of Papua have a deep connection with the land and the natural world, and their cultures are characterized by a strong sense of community and spirituality. Some of the major ethnic groups in Papua include the Dani, the Asmat, and the Korowai.
The people of Papua are known for their traditional clothing, which is often made from natural materials such as leaves, grasses, and animal hides. The traditional clothing is often decorated with intricate patterns and designs, which are used to signify status, wealth, and cultural identity. The people of Papua are also known for their traditional music and dance, which is often performed during ceremonies and celebrations.
Wildlife and Conservation
Papua is home to some of the most diverse and unique wildlife in the world, including birds, mammals, reptiles, and insects. The province is home to over 600 species of birds, including the iconic bird of paradise, which is found only in Papua. The province is also home to a range of mammals, including tree kangaroos, wallabies, and pigs. The coral reefs off the coast of Papua are home to a stunning array of marine life, including fish, turtles, and sharks.
Despite the rich biodiversity of Papua, the province is facing a range of conservation challenges, including deforestation, habitat destruction, and hunting. The Indonesian government has established a number of national parks and protected areas in Papua, including the Lorentz National Park, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. However, more needs to be done to protect the unique and fragile ecosystems of Papua, and to ensure the long-term conservation of the province’s wildlife.
Economy and Infrastructure
The economy of Papua is primarily based on agriculture, with crops such as rice, maize, and sweet potatoes being major staples. The province is also rich in natural resources, including gold, copper, and oil. The mining industry is a significant contributor to the economy of Papua, with a number of major mining operations located in the province. However, the mining industry has also been the subject of controversy and criticism, with concerns over environmental damage and social impacts.
The infrastructure in Papua is limited, with many areas of the province lacking access to basic services such as roads, electricity, and healthcare. The Indonesian government has invested heavily in infrastructure development in Papua, including the construction of new roads, bridges, and airports. However, more needs to be done to improve the infrastructure in Papua, and to ensure that the province is connected to the rest of Indonesia and the world.
Tourism and Travel
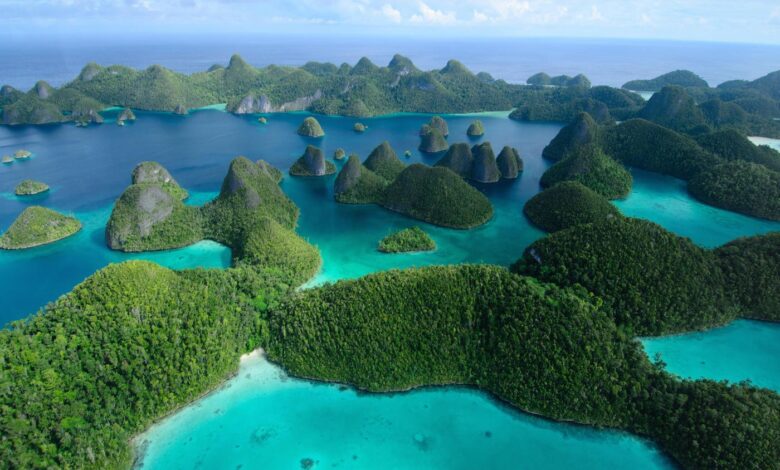
Papua is a popular destination for tourists and travelers, with a range of attractions and activities on offer. The province is home to some of the most beautiful and pristine natural landscapes in the world, including the Baliem Valley, the Puncak Jaya mountain range, and the Raja Ampat archipelago. The province is also home to a range of cultural attractions, including traditional villages, museums, and festivals.
However, traveling in Papua can be challenging, with limited infrastructure and a range of safety concerns. The province has experienced periods of civil unrest and conflict, and there are concerns over crime and security. Travelers to Papua should exercise caution and carefully plan their trip, and should consider working with a reputable tour operator or guide.
History and Politics
Papua has a complex and tumultuous history, with the province being colonized by the Dutch in the 19th century. The province was annexed by Indonesia in 1963, and has since been the subject of a range of political and social tensions. The province has experienced periods of civil unrest and conflict, including the Papua conflict, which began in the 1960s and continues to this day.
The Indonesian government has implemented a range of policies and programs aimed at promoting development and stability in Papua, including the establishment of the Papua Special Autonomy Law in 2001. However, the law has been criticized for failing to address the underlying causes of the conflict, and for not providing sufficient autonomy and self-governance to the people of Papua.
Challenges and Opportunities
Papua faces a range of challenges, including poverty, inequality, and limited access to basic services such as healthcare and education. The province is also vulnerable to a range of environmental challenges, including deforestation, climate change, and natural disasters. However, Papua also has a range of opportunities, including the potential for sustainable development, cultural preservation, and environmental conservation.
The Indonesian government and international organizations are working to address the challenges facing Papua, and to promote development and stability in the province. This includes initiatives such as the Papua Development Acceleration Program, which aims to promote economic development and improve living standards in the province.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Papua is a unique and fascinating province, with a rich cultural heritage, diverse wildlife, and breathtaking natural landscapes. The province faces a range of challenges, including poverty, inequality, and limited access to basic services. However, Papua also has a range of opportunities, including the potential for sustainable development, cultural preservation, and environmental conservation. By working together, the Indonesian government, international organizations, and local communities can promote development and stability in Papua, and ensure a bright future for the people of this incredible province.
Recommendations for Travelers
If you are planning to travel to Papua, here are some recommendations to keep in mind:
- Research and planning: Research the province and its culture, and plan your trip carefully. Consider working with a reputable tour operator or guide.
- Safety and security: Exercise caution and be aware of your surroundings, especially in areas with high crime rates or civil unrest.
- Respect for local culture: Respect the local culture and traditions, and be mindful of cultural sensitivities.
- Environmental awareness: Be aware of the environmental challenges facing Papua, and take steps to minimize your impact on the environment.
- Support for local communities: Support local communities and businesses, and consider donating to organizations that work to promote development and conservation in Papua.
Further Reading and Resources
For more information on Papua, here are some recommended resources:
- Books: “Papua: A History” by John Saltford, “The Papua Conflict” by Richard Chauvel.
- Articles: “Papua: A Province in Transition” by the Jakarta Post, “The Future of Papua” by the Indonesian Times.
- Websites: The official website of the Papua Provincial Government, the Papua Tourism Board, and the Indonesian Ministry of Tourism.
- Organizations: The Papua Development Acceleration Program, the Indonesian Red Cross, and the World Wildlife Fund.
Appendix

This appendix provides additional information on Papua, including a glossary of terms, a list of major ethnic groups, and a timeline of major events in the province’s history.
Glossary of Terms
Here is a glossary of terms related to Papua:
- Papua: The easternmost province of Indonesia, located on the island of New Guinea.
- Western New Guinea: The western half of the island of New Guinea, which is part of Indonesia.
- Indigenous people: The native people of Papua, who have lived in the province for thousands of years.
- Special autonomy: A form of autonomy granted to Papua by the Indonesian government, which provides for greater self-governance and decision-making power.
Major Ethnic Groups
Here is a list of major ethnic groups in Papua:
- Dani: A major ethnic group in Papua, known for their traditional clothing and cultural practices.
- Asmat: A major ethnic group in Papua, known for their traditional wood carvings and cultural practices.
- Korowai: A major ethnic group in Papua, known for their traditional treehouse dwellings and cultural practices.
Timeline of Major Events
Here is a timeline of major events in the history of Papua:
- 19th century: Papua is colonized by the Dutch.
- 1963: Papua is annexed by Indonesia.
- 1960s: The Papua conflict begins, with indigenous people fighting for independence and self-governance.
- 2001: The Papua Special Autonomy Law is established, providing for greater autonomy and self-governance in the province.